
Examples of accrued expenses include wages payable, interest payable, and rent expenses. By far the most important equation in credit accounting is the debt ratio. It compares your total liabilities to your total assets to tell you how leveraged—or, how burdened by debt—your business https://www.instagram.com/bookstime_inc is. Liabilities are found on the right side or lower half of a balance sheet. A common small business liability is accounts payable, or money owed to suppliers.
- Examples of accrued expenses include wages payable, interest payable, and rent expenses.
- Common examples of equity include retained earnings, paid-in capital, and share capital.
- Contingent liabilities are liabilities that may result based on the outcome of a future event such as the outcome of a lawsuit, injuries from product use, or honoring product warranties.
- The portion of the vehicle that you’ve already paid for is an asset.
- Knowing what a liability is and how it functions in the accounting process is necessary to properly manage the financials of any business.
Type 2: Mortgage payable

Some examples of short-term liability include credit card debt, insurance premiums payable, payroll taxes, or staff wages. However, an expense can create a liability if the expense is not immediately paid. For instance, when you receive a utility list of liabilities in accounting bill, you must record the utility expense.
See advice specific to your business
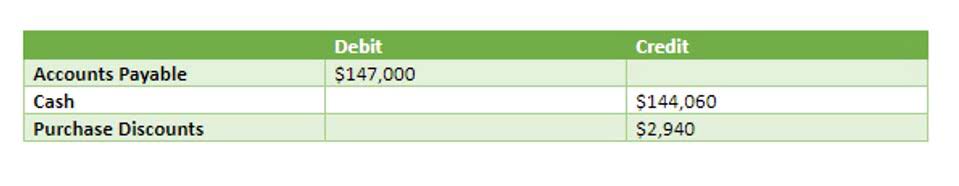
- This common practice generally results in a large accounts payable liability.
- One of the few examples of a contra liability account is the discount on bonds payable (or notes payable) account.
- Based on their durations, liabilities are broadly classified into short-term and long-term liabilities.
- The ratio, which is calculated by dividing current assets by current liabilities, shows how well a company manages its balance sheet to pay off its short-term debts and payables.
- In short, liabilities are the opposite of total assets a company owns.
- The operating cycle refers to the period of time it takes for the business to turn its inventory into sales revenue and then back into cash, which helps cover these expenses.
Here, we cover the various aspects of liabilities to better understand your business’s accounting side. As a small business, you need to manage your business accounting accurately. Continue reading to understand how to calculate liabilities for your business.. Liabilities refer to short-term and long-term obligations of a company. Unearned revenue is money that has been received by a customer in https://www.bookstime.com/ advance of goods and services delivered.
How are liabilities used in calculating a company’s net worth?

The quick ratio is a more conservative measure for liquidity since it only includes the current assets that can quickly be converted to cash to pay off current liabilities. The balance sheet which records the assets, liabilities, and equity of a company is sometimes referred to as a statement of net worth or a statement of financial position. This is because it summarizes the financial position of a firm at a glance, showing all the assets, liabilities, and equity. An expense is the cost of operations that a company incurs to generate revenue. In accounting, assets are what a company owns, while liabilities are what a company owes. Liabilities are usually found on the right side of the balance sheet; assets are found on the left.
- Calculating liabilities is not that complicated – you need to record all your liabilities carefully and add them up in your balance sheet.
- The latter is an account in which the company maintains all its records such as debts, obligations, payable income taxes, customer deposits, wages payable, and expenses incurred.
- The money you owe is considered a liability until you pay off the invoice.
- A business’s liabilities can be examined in a variety of ways to determine its overall health and long-term viability.
- Understanding a company’s liabilities can also help assess its ability to meet debt obligations and the potential for future growth.
- Keep up with Michelle’s CPA career — and ultramarathoning endeavors — on LinkedIn.
- Most contingent liabilities are uncommon for small businesses, but here are some that you might encounter.
- And this can be to other businesses, vendors, employees, organizations or government agencies.
- Your business has unearned revenue when a customer pays for goods or services in advance.
- Try FreshBooks for free by signing up today and getting started on your path to financial health.
- As mentioned, a liability is anything your company owes, and typically this is money.
Contingent liabilities are potential future obligations that depend on the occurrence of a specific event or condition. These liabilities may or may not materialize, and their outcome is often uncertain. Examples of contingent liabilities include warranty liabilities and lawsuit liabilities. This can give a picture of a company’s financial solvency and management of its current liabilities. Contingent liabilities are liabilities that may result based on the outcome of a future event such as the outcome of a lawsuit, injuries from product use, or honoring product warranties.


